| [1]季少平.少突胶质细胞分化的分子机理研究进展[J],河南大学学报:医学版),2012,31(1):1-4.
[2]Bradl M,Lassmann H.Oligodendrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119(1):37-53.
[3]Tokumoto YM, Apperly JA, Gao FB, et al. Posttranscriptional regulation of p18 and p27 Cdk inhibitor proteins and the timing of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Dev Biol.2002;245(1): 224-234.
[4]He L, Lu QR. Coordinated control of oligodendrocyte development by extrinsic and intrinsic signaling cues. Neurosci Bull.2013;29(2):129-143.
[5]蒋萌,胡怀强,林晓静.少突胶质前体细胞分化的调节机制[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012, 8(1): 56-59.
[6]Raff MC, Durand B, Gao FB. Cell number control and timing in animal development: the oligodendrocyte cell lineage. Int J Dev Biol.1998, 42(3):263-267.
[7]Larocque D, Galarneau A, Liu HN, et al. Protection of p27(Kip1) mRNA by quaking RNA binding proteins promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(1):27-33.
[8]Tang XM, Strocchi P, Cambi F. Changes in the activity of cdk2 and cdk5 accompany differentiation of rat primary oligodendrocytes.J Cell Biochem.1998;68(1):128-137.
[9]Ghiani C, Gallo V. Inhibition of cyclin E-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 complex formation and activity is associated with cell cycle arrest and withdrawal in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J Neurosci.2001;21(4):1274-1282.
[10]Frederick TJ, Wood TL. IGF-I and FGF-2 coordinately enhance cyclin D1 and cyclin E-cdk2 association and activity to promote G1 progression in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci.2004;25(3):480-492.
[11]Miyamoto Y,Yamauchi J,Chan JR,et al.Cdk5 regulates differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells through the direct phosphorylation of paxillin[J]. J Cell Sci.2007;120(24): 4355-4366.
[12]Besset V, Rhee K, Wolgemuth DJ. The identification and characterization of expression of Pftaire-1, a novel Cdk family member, suggest its function in the mouse testis and nervous system. Mol Reprod Dev.1998;50(1):18-29.
[13]Ahrendsen JT, Macklin W. Signaling mechanisms regulating myelination in the central nervous system. Neurosci Bull. 2013; 29(2):199-215.
[14]Wood TL, Bercury KK, Cifelli SE, et al. mTOR: a link from the extracellular milieu to transcriptional regulation of oligodendrocyte development. ASN Neuro. 2013;5(1): e00108.
[15]Shu F, Lv S, Qin Y, et al. Functional characterization of human PFTK1 as a cyclin-dependent kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(22):9248-9253.
[16]Sun T, Co NN, Wong N. PFTK1 interacts with cyclin Y to activate non-canonical Wnt signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2014; 449(1):163-168.
[17]Pang EY, Bai AH, To KF, et al. Identification of PFTAIRE protein kinase 1, a novel cell division cycle-2 related gene, in the motile phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.2007;46(2):436-445.
[18]Jiang M, Gao Y, Yang T, et al. Cyclin Y, a novel membrane- associated cyclin, interacts with PFTK1. FEBS Lett. 2009; 583(13):2171-2178.
[19]Guardiola-Diaz HM,Ishii A,Bansal R.Erk1/2 MAPK and mTOR signaling sequentially regulates progression through distinct stages of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Glia.2012;60(3): 476-486.
[20]Buckinx R, Smolders I, Sahebali S, et al. Morphological changes do not reflect biochemical and functional differentiation in OLN-93 oligodendroglial cells. J Neurosci Methods.2009;184(1):1-9. |
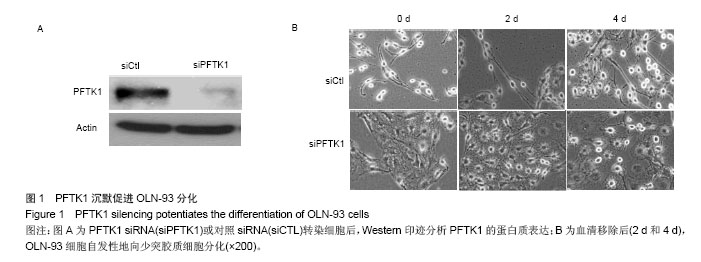
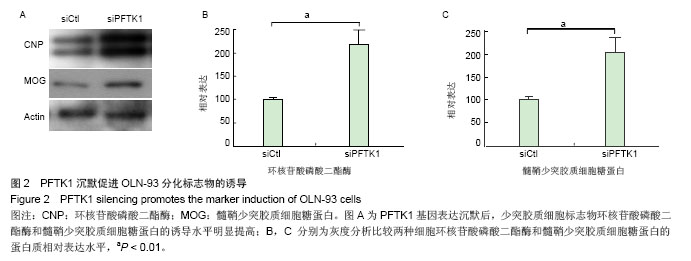
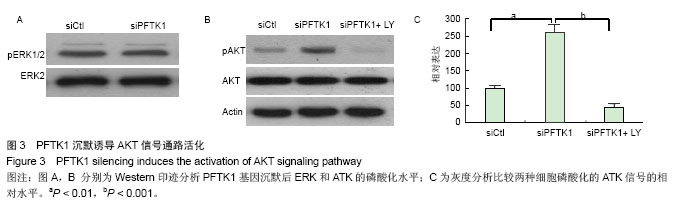
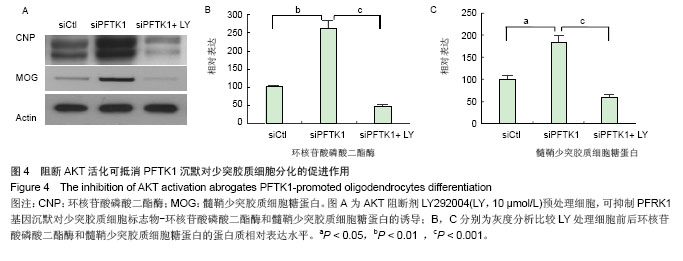
.jpg)